The Republic of India, referred to as "India", is located in South Asia. It is the world's second largest software power, the world's largest outsourcing service recipient country, and the largest country in the South Asian subcontinent. In the northeast, it borders China, Nepal and Bhutan. Bangladesh is sandwiched between the northeastern territory. In the east, it is adjacent to Myanmar. In the southeast, it faces Sri Lanka across the sea. In the northwest, it borders Pakistan. It faces the Bay of Bengal in the east and the Arabian Sea in the west.
India claims to have 29 states and 7 union territories, with its capital being New Delhi.
Main Religions: Hinduism, Islam, Sikhism.

In India, the relationship between employers and employees is recorded through formal employment contracts. The contracts may contain additional terms such as non-compete and confidentiality agreements to ensure clear rights and obligations for both parties. According to Indian labor regulations, when enterprises draft a "Model Labor Contract", the following 5 to 10 items should be included:
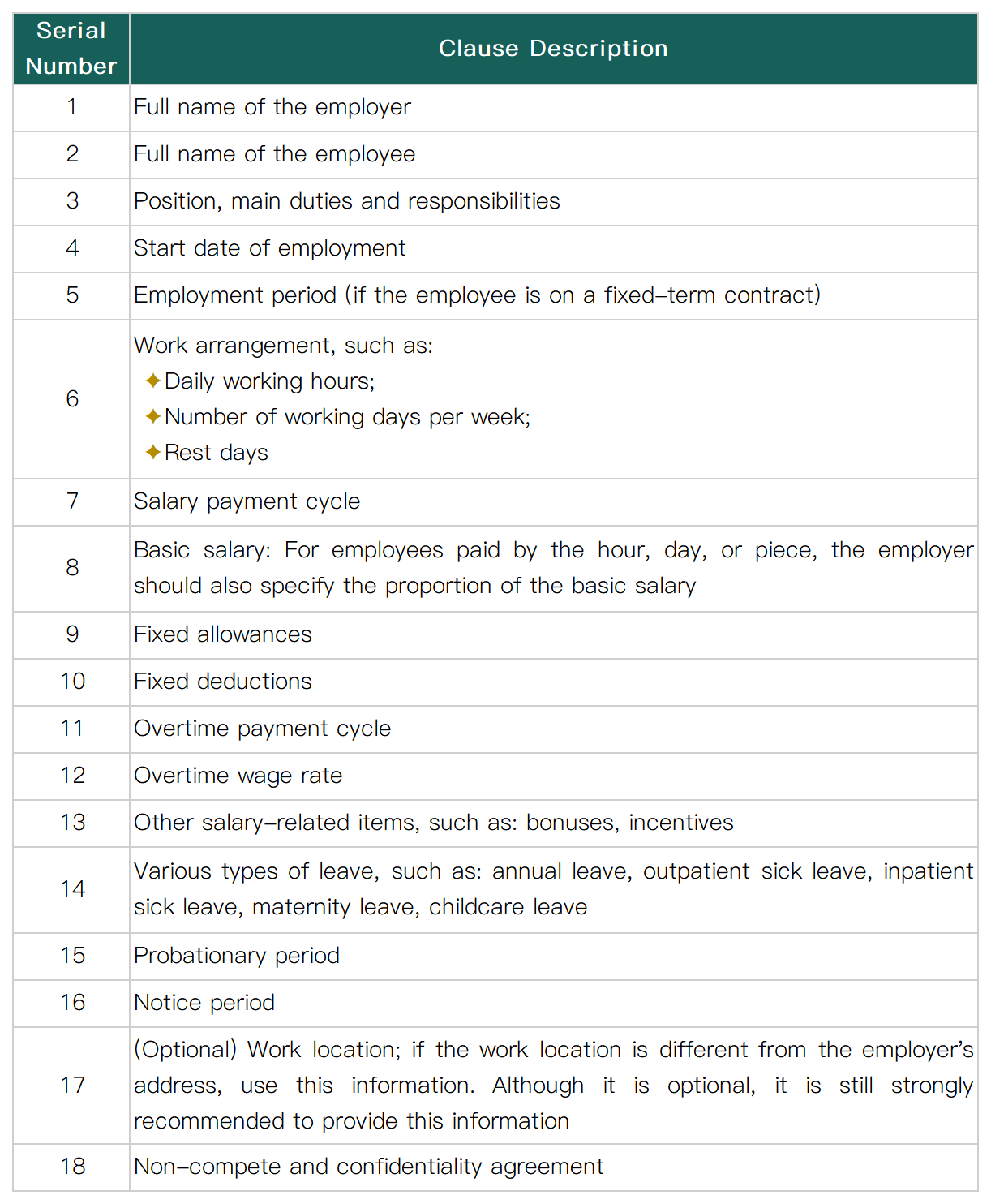
The employment contract can be oral or written. If the contract is in written form, all employers must provide a copy of the written employment contract to the employee. In addition, the employer must obtain the consent of the employee before making any subsequent changes to the terms of the employment contract. Signing a written contract is not mandatory. An oral contract still refers to the act. Therefore, workers are protected.
In India, the maximum probationary period is not more than six months. During the probationary period, the employer can terminate the employment relationship at any time without prior notice or payment of compensation. However, if an employee suffers discrimination or abuse during the probationary period, he or she can file a lawsuit with the labor court.
India is a multi-religious country with a large number of festivals, which can be generally divided into four categories: political festivals, seasonal festivals, historical festivals and religious festivals. There are more than 20 major festivals every year, such as Republic Day, Independence Day, Holi and Diwali.
In 2024, there are a total of 18 national statutory holidays in India. The main holidays are as follows in the table:
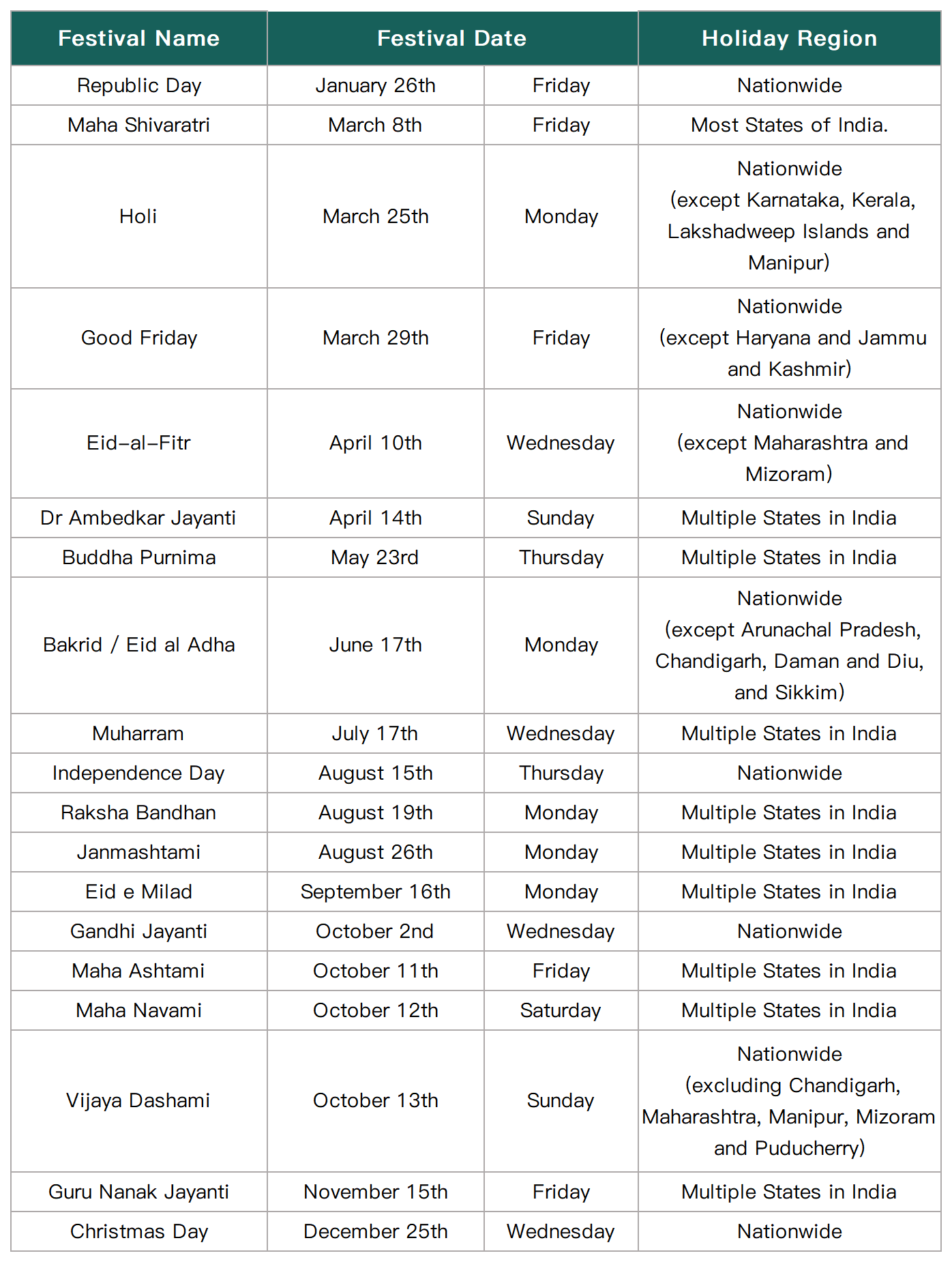
* The table shows the major national holidays and some state-level holidays in 2024. However, public offices inside and outside Delhi do not enjoy all these holidays. The latest specific holiday times are subject to official announcements. This article is for reference only.
1.Standard Working Hours:
✦ Generally, it is 8 hours per day, with a maximum of no more than 9 hours. The maximum is 48 hours per week.
✦ In some regions, it is 9 hours per day and the maximum is 48 hours per week.
2.Rest Time:
✦ Employees who work continuously for 4 to 5 hours can get a 30-minute to 1-hour meal break.
✦ Employees cannot work without a break for more than 6 hours.
✦ Employees on shift work should have at least one full day off per week or can rest for 12 hours between two shifts.
3.Night Shift Time:
✦ Night shift time: Usually between 7 pm and 6 am. However, some states will have a stricter definition of night shift time, such as between 10 pm and 6 am.
✦ Salary standard: 1.25 times the hourly wage.
4.Overtime Hours:
✦ Overtime requirements: Overtime hours should not exceed 2 hours per day and 12 hours per week.
✦ Overtime compensation:
A、Overtime on standard working days: Paid at twice the standard wage.
B、Overtime on weekends/holidays: Paid at three times the standard wage.
1.Paid Annual Leave:
✦ Applicable situation: Employees who have worked continuously for one year with the same employer.
✦ Number of leave days: At least 21 days, but the standards may vary in different industries or regions.
✦ Regional differences: Some states such as Tamil Nadu stipulate at least 26 days of annual leave, while Jharkhand only stipulates at least 12 days.
2.Sick Leave:
✦ Applicable situation: Employees who are unable to work due to illness or injury.
✦ Number of leave days: At least 12 days of paid sick leave per year, but there are also regional differences.
✦ Regional differences: For example, Gujarat stipulates at least 14 days of sick leave per year, while Assam has at least 10 days.
3.Casual Leave/Personal Leave:
✦ Applicable situation: Employees who need leave due to emergencies or personal reasons.
✦ Number of leave days: At least 12 days of casual leave per year, and in some places it can reach 15-20 days.
✦ Regional differences: Delhi stipulates at least 15 days of casual leave, while Rajasthan has 12 days.
In addition, there are other special leaves such as maternity leave, marriage leave, and bereavement leave. Their standards may also vary slightly depending on the region. In general, India's legal leave system is quite perfect and fully considers various work and life needs.
The Income Tax Department of India is managed by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) and is part of the tax department under the Ministry of Finance. The taxation of individuals in India is mainly based on their residential status in the relevant tax year. The following is an explanation of the types of individual residential status:
✦ Resident and Ordinarily Resident (ROR): This refers to an individual who resides in India during the relevant tax year. The taxation scope of ROR covers their global income, regardless of where it is earned.
✦ Resident but Not Ordinarily Resident (RNOR): This refers to an individual who resides in India during the relevant tax year but has not resided in India as an ordinarily resident in the past few years. For RNOR, taxation in India is only required if their income is generated in India, is deemed to be generated in India, is deemed to be received in India, or comes from a business controlled in India or an established profession.
✦ Non-Resident (NR): This refers to an individual who does not reside in India during the relevant tax year. Non-residents only need to pay Indian taxes on their income generated in India, deemed to be generated in India, received or deemed to be received in India.
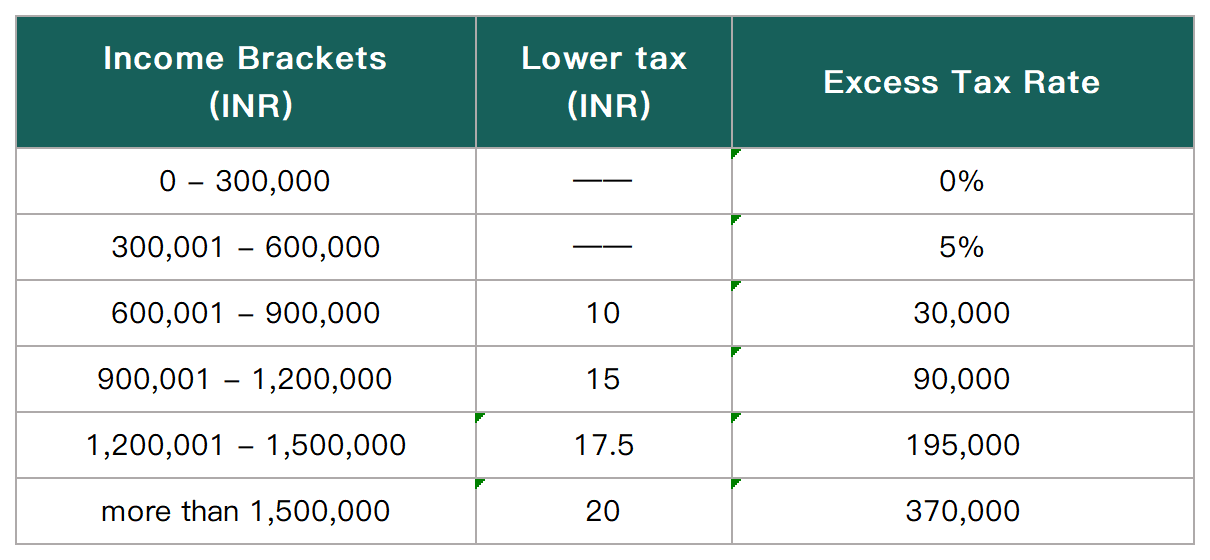
* The 2023 budget has expanded the scope of personal annual income exemption under the new income tax system to 700,000 Indian rupees. Previously, individuals with an annual income of less than 500,000 Indian rupees did not need to pay income tax under either the old or new system. In addition, the new income tax system includes a standard deduction of 50,000 Indian rupees, allowing salaried taxpayers to deduct 50,000 Indian rupees in advance from their total taxable income, which was previously only possible under the old system.
India's social security system is composed of various schemes and plans and is covered by various laws and regulations. These social security plans aim to provide economic and social protection for India's labor force. The following are several types of social insurance covered by India's social security plans.
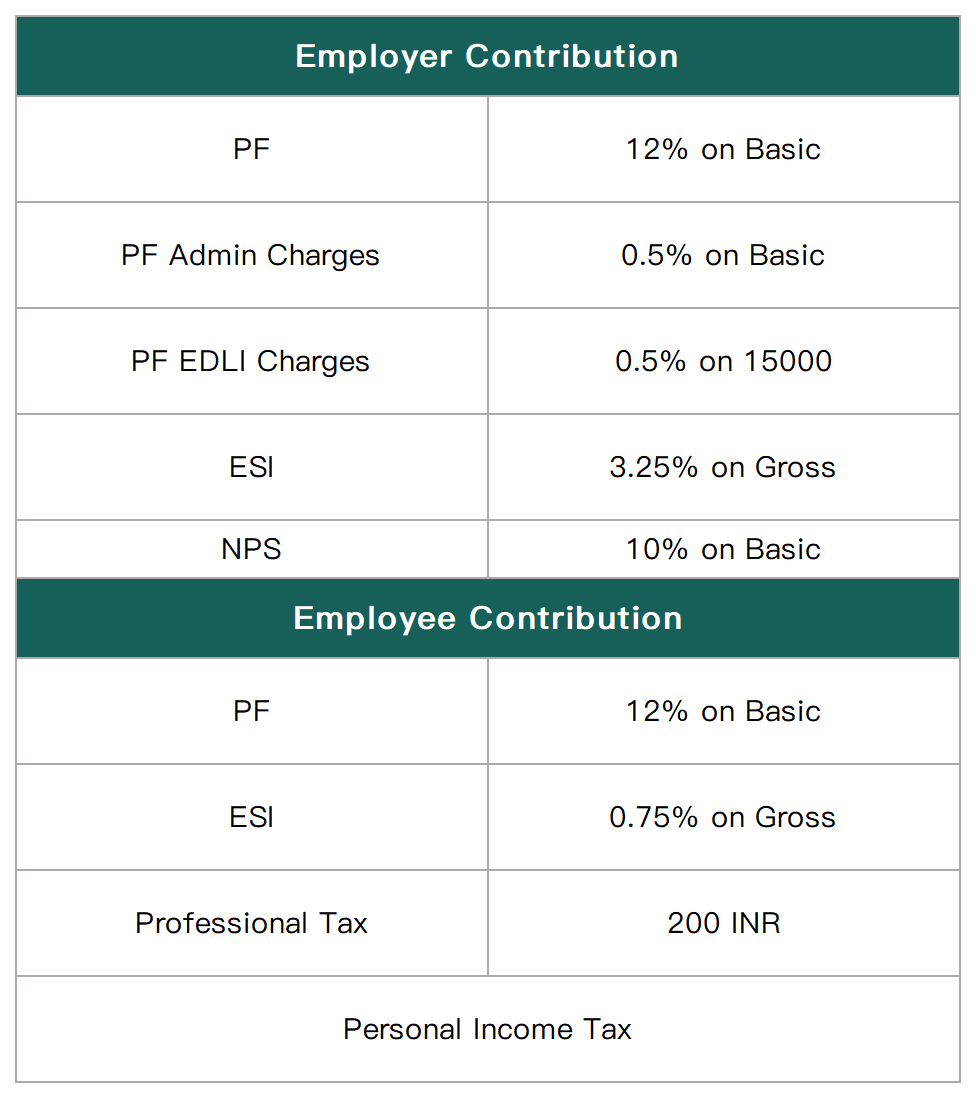
* The specific proportions and amounts may change over time and according to policy. Therefore, it is recommended to check the latest laws and regulations or consult professionals to obtain accurate information.
1.Contract Termination Notice:
✦ Any termination notice given by the employee or the employer must be in writing, otherwise it will be considered invalid.
2.Notice Period:
✦ Short-term/fixed-term labor contract, usually 1-3 months, which is determined by the contract.
3.Compensation:
✦ Basis for calculating severance pay: The calculation of severance pay is based on the employee's basic salary and does not include allowances and other parts. Basic salary usually refers to an employee's fixed monthly salary or hourly wage.
✦ Severance pay calculation formula:
Severance pay = Basic salary × Notice period for resignation
For example: If an employee's basic salary is 20,000 rupees per month and the notice period for resignation is 2 months, then the severance pay is 40,000 rupees.
 EOR
EOR GREC
GREC VISA
VISA PAYROLL
PAYROLL



 Home
Home
 Solutions
Solutions
 Resources
Resources
 Contact
Contact