The Federal Republic of Germany (Federal Republic of Germany), referred to as Germany, with its capital Berlin. It is located in central Europe. It is bordered by Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, the Netherlands, Belgium, Luxembourg and France to the west, and Denmark to the north, bordering the North Sea and the Baltic Sea.
Germany is a highly developed industrialized country, the world's third-largest economy, the largest economy and market in Europe, and the world's third-largest exporter. It is an important member of international organizations such as the European Union and NATO.
Main Religions: Protestantism, Catholicism.

In Germany, the legal framework of labor contracts is mainly stipulated by the German Civil Code (BGB) and the Labor Law. The following are the specific situations regarding labor contracts:
1、Contract Duration:
✦ Fixed-term contract: According to the "Law on Fixed-term Labor Contracts", the renewal of fixed-term contracts has certain restrictions. Usually, the renewal shall not exceed twice, and the total duration shall not exceed two years.
✦ Open-ended contract: The contract has no definite end date. It is the most common type of labor contract in Germany and provides higher job security.
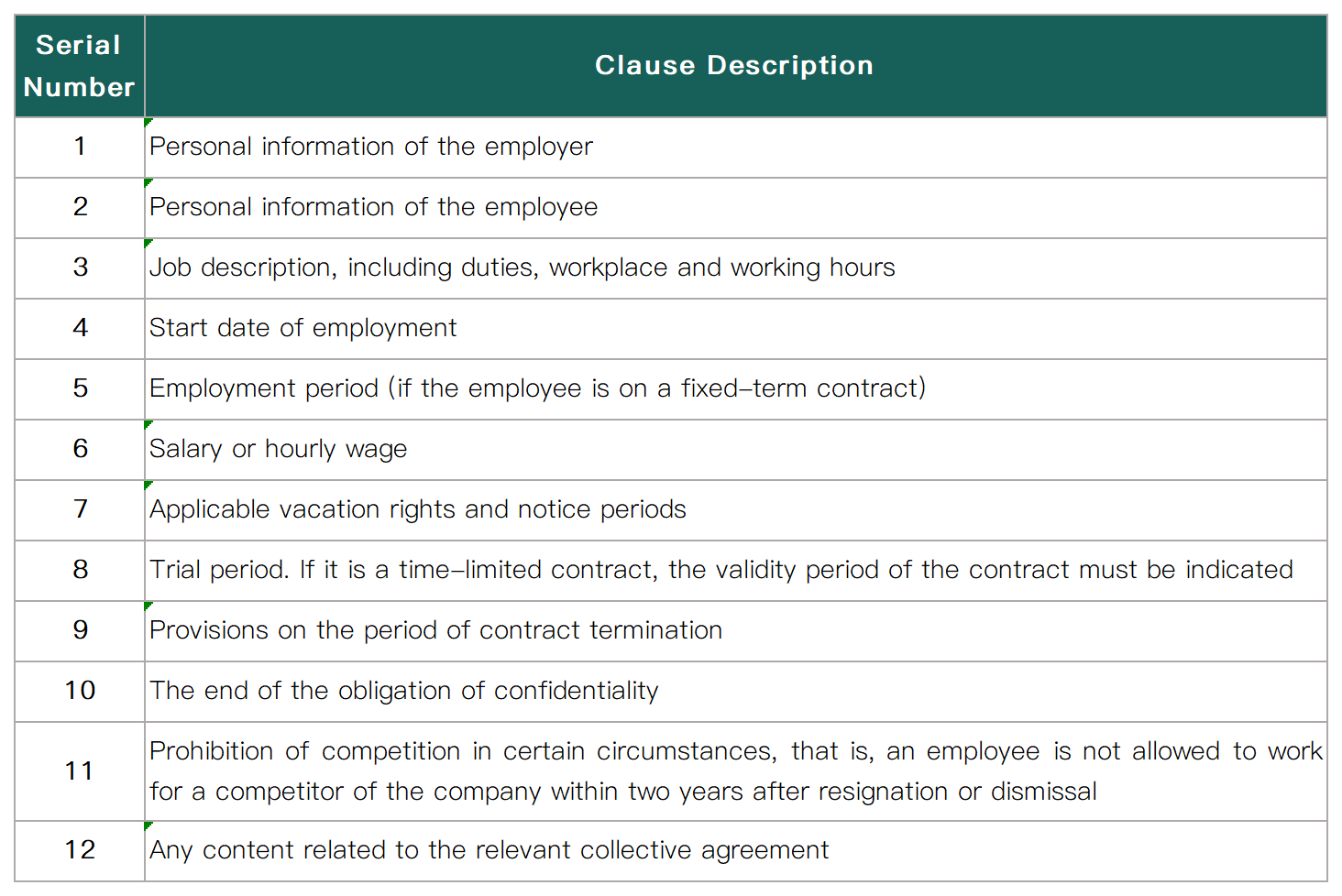
2、Details mainly included in the contract:
3、Forms and cycles of salary payment:
✦ Under normal circumstances, the salary payment cycle is once a month, usually paid on or around the 25th of each month. Other specific payment dates can also be set according to the labor contract or company regulations. The payment cycle should be clearly stipulated in the employment agreement;
✦ Salaries can be paid through various methods, including direct deposit, cheque or cash payment, etc. Among them, direct deposit is the most common payment method. Employers usually require employees to provide valid bank account information for salary deposit;
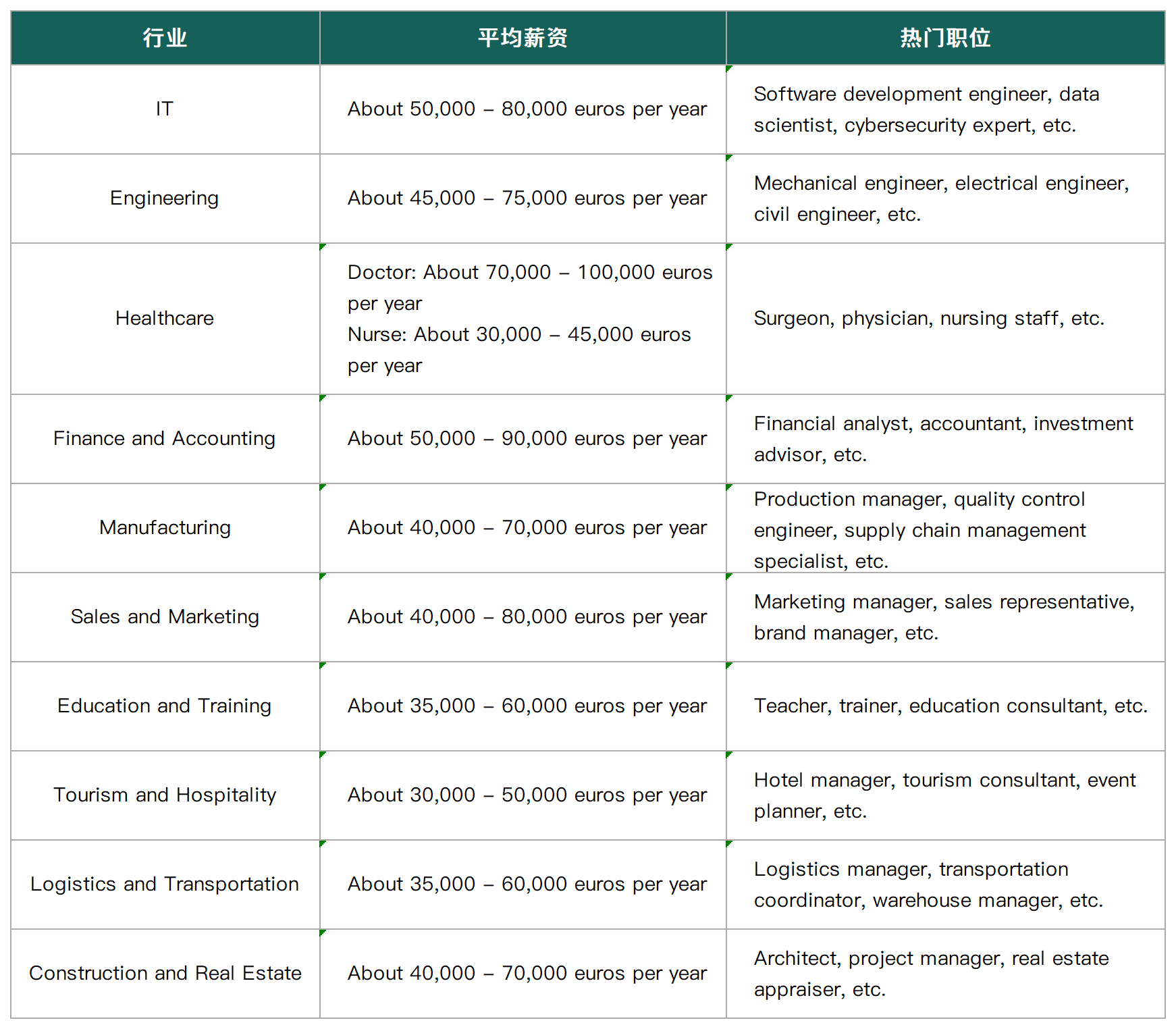
✦ Popular industries and average salaries in Germany:
✦ It is usually 6 months, but it can vary according to the company's policies and industry standards.
✦ Employees during the probationary period enjoy the same basic rights as regular employees (such as salary, vacation, etc.).
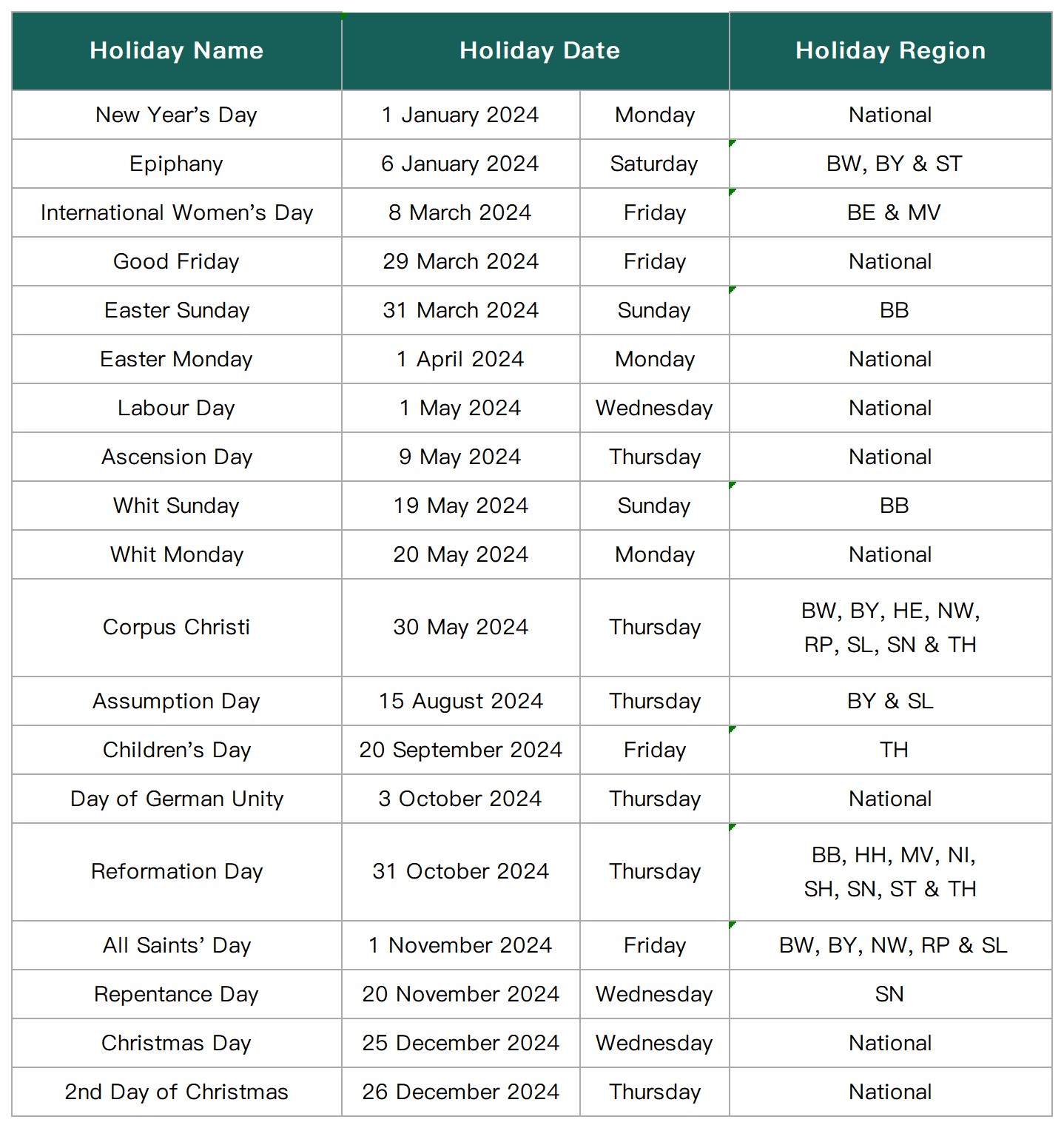
Public holidays in Germany are not regulated at the federal level and vary from state to state. There are a total of 9 public holidays across the country in 2024.
1. Standard working hours:
✦ Working hours per week: Generally 40 hours, but it may vary depending on the industry and the company's policies;
✦ Daily working hours: Usually no more than 8 hours. If an employee needs to work more than 8 hours, the relevant regulations on overtime must be followed.
2. Rest time:
✦ Daily rest: Employees who work for more than 6 hours should have at least 30 minutes of rest time; employees who work for more than 9 hours should have at least 45 minutes of rest time.
✦ Rest arrangement: The rest time can be divided into multiple stages, but it must be arranged during working hours and should be taken within the first 6 hours of the start of work.
✦ Weekly rest: Employees should have at least one continuous rest period per week, usually 48 hours (that is, two days).
3. Night shift time:
✦ Night shift time: Usually the working hours between 11 p.m. and 6 a.m., and generally the night shift time does not exceed 8 hours.
✦ Salary standard: Night shift wages are usually between 125% and 150% of the normal wage, depending on the company policy and collective agreement; some industries (such as medical care, transportation, etc.) may have higher night shift compensation standards.
✦ Additional compensation: Employers usually provide regular health checks for night shift employees to ensure their physical health.
4. Overtime hours:
✦ Overtime requirements: The total working hours of overtime shall not exceed the legal daily and weekly working hour limits.
✦ Overtime compensation fee: Usually 125% to 150% of the normal wage.
✦ Compensation method:
A. Generally, compensation is made in the form of overtime pay.
B. Some companies allow employees to choose to be compensated in the form of compensatory leave instead of overtime pay. Usually, it is calculated based on the proportion of overtime hours. For example, 1 hour of overtime can be exchanged for 1.25 hours of compensatory leave (if the overtime pay is 125%).
Germany is a country with a rich vacation system. The annual leave system is very complete, and workers and employees enjoy sufficient vacation time, which helps protect the rights and interests of workers and promote the balance between work and life.
1. Annual leave:
✦ If an employee works 6 days a week, the annual leave is 2 days per month, with at least 24 days of vacation. If the employee works 5 days a week, the annual leave is 1.67 days per month.
✦ Most employees have an average of 30 days of vacation each year.
✦ During the probationary period, employees are usually also entitled to annual leave, but it may be subject to certain restrictions.
2. Sick leave:
✦ Employees are entitled to 6 weeks (42 days) of sick leave only after they have been employed for 4 weeks, and the employer must pay them at least their full salary for 6 weeks.
✦ If the sick leave exceeds six weeks, the employee will be transferred to receive sick pay from the health insurance company, which is generally 70% of the salary, but not exceeding the legal maximum limit.
3. Personal leave:
✦ Employees can take 3-5 days within a year to handle urgent family affairs and receive normal wages at the same time. The specific details should be stated in the employment contract.
In addition, there are other special leaves such as maternity leave, parental leave, care leave, and bereavement leave. Overall, German labor law provides various types of leaves, aiming to protect the rights and interests of employees and ensure they maintain a balance between work and life. Although most leave regulations are unified nationwide, individual industries or companies may offer more generous conditions based on collective agreements.
Income tax in Germany is paid throughout the year in the form of "wages". In most cases, if an individual resides continuously in Germany for more than 6 months, they must submit a tax return to the local tax bureau. Personal income tax in Germany is calculated based on a progressive tax rate, and the tax rate gradually increases with the income level. The specific tax rate and tax exemption amount for personal income tax vary depending on an individual's income and family status. Personal income tax in Germany is mainly collected through the method of "prepayment in installments, final summary accounting and settlement at the end of the year, with refunds for overpayment and additional payment for underpayment". For income such as wages, interest, dividends and bonuses, the withholding method is used for source taxation.
Different degrees of tax deductions can be obtained according to marital status and the number of children. The following are the progressive tax rate ranges in Germany in 2024:
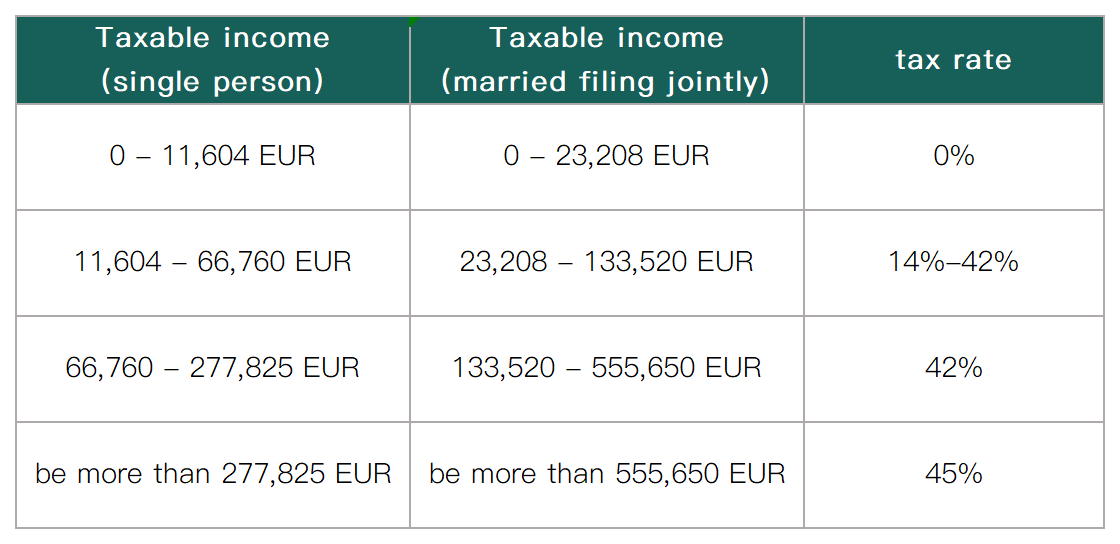
* The above are the latest personal income tax data. Please note that the applicable standards and tax rates may change according to the updates of German tax laws. It is recommended that you check the official website of the country at any time or contact us to obtain the latest data.
In addition to the above tax rates, the following surtaxes are levied on all types of income:
✦ The church tax in Germany is a special taxation system applicable to those German citizens who are Christian. The tax rate of the church tax varies by region and is approximately 8-9% of the income tax. The church tax is based on an individual's religious belief and is used to support the operations and activities of various churches. It should be noted that the church tax is voluntary and only applicable to those who voluntarily join the church and register as church members. For those who do not believe in Christianity or are not registered as church members, they do not need to pay the church tax.
✦ The German Solidarity Surcharge is a temporary tax aimed at financing the reconstruction and development of the eastern German regions (former East Germany). This tax was introduced in 1991 and was initially designed to address the economic and social challenges brought about by German reunification. The Solidarity Surcharge is calculated based on the taxpayer's income tax, corporate tax and capital gains tax. Those with an annual income of more than 109,000 euros need to pay the full rate of 5.5%, while those with an income of no more than 73,000 euros do not need to pay. The tax is calculated and paid by taxpayers when filing tax returns. According to the government's decision, starting from January 1, 2021, the Solidarity Surcharge has begun to be gradually abolished. The abolition process will be divided into several stages, reducing the collection rate year by year, and finally completely abolishing the Solidarity Surcharge in 2025.
In Germany, there are some categories of income that can enjoy tax-exempt treatment. This includes specific payments from health or accident insurance and certain social security benefits, such as unemployment benefits and maternity grants. Additionally, kindergarten fees that meet specific conditions can also be tax-exempt. Moreover, if a second home is established in Germany for business purposes, certain payments can also enjoy tax exemption. These payments include home travel (once a week), meal allowances (up to a certain amount and time-limited), and rent for the workplace (actual expenses, but no more than 1,000 euros per month). For rent, meal allowances and commuting expenses incurred by employees, tax-free reimbursements are usually possible based on meeting specific conditions.
It should be noted that wage tax is withheld and paid by the employer from the salary on a monthly basis, while other types of income may be assessed by the authorities based on individual circumstances and paid by the individuals themselves. For the interest, dividends and capital gains of stocks, a uniform tax of 25% and an additional solidarity fee need to be paid. These tax-exempt regulations are designed to provide certain economic benefits and welfare to ensure that individuals can enjoy certain tax deductions in specific circumstances.
The social insurance system in Germany is very comprehensive, including medical insurance, supplementary medical insurance, long-term care insurance, pension insurance and unemployment insurance. For details, please refer to the following table:
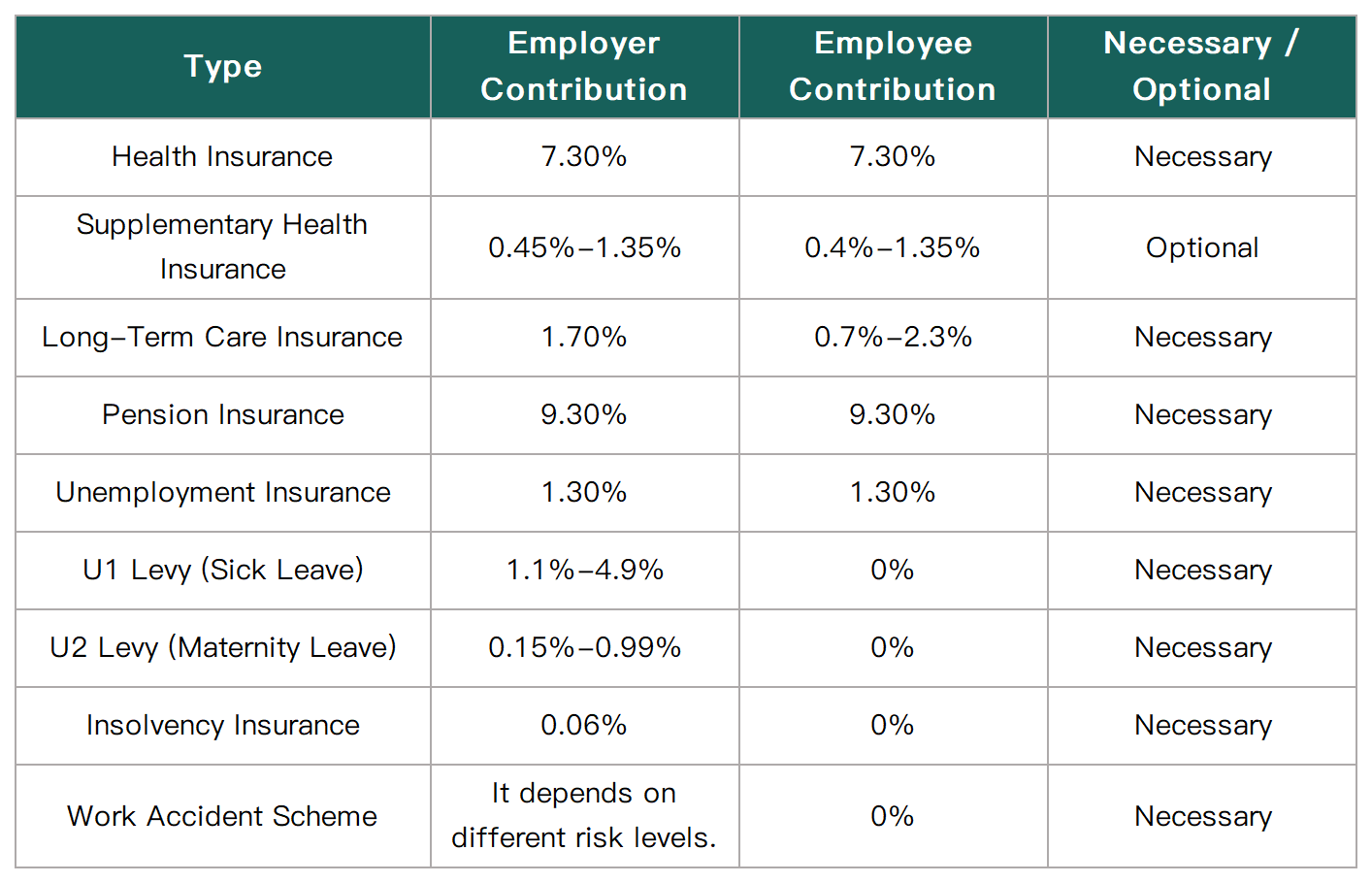
* The social insurance system in Germany is relatively complex. The specific contribution ratios and regulations may be adjusted. It is recommended to pay attention to the latest local policies and regulations. This article is for reference only.
1. Notice of Contract Termination:
✦ Any termination notice issued by the employee or the employer must be sent in written form as a notice letter; otherwise, it will be regarded as invalid.
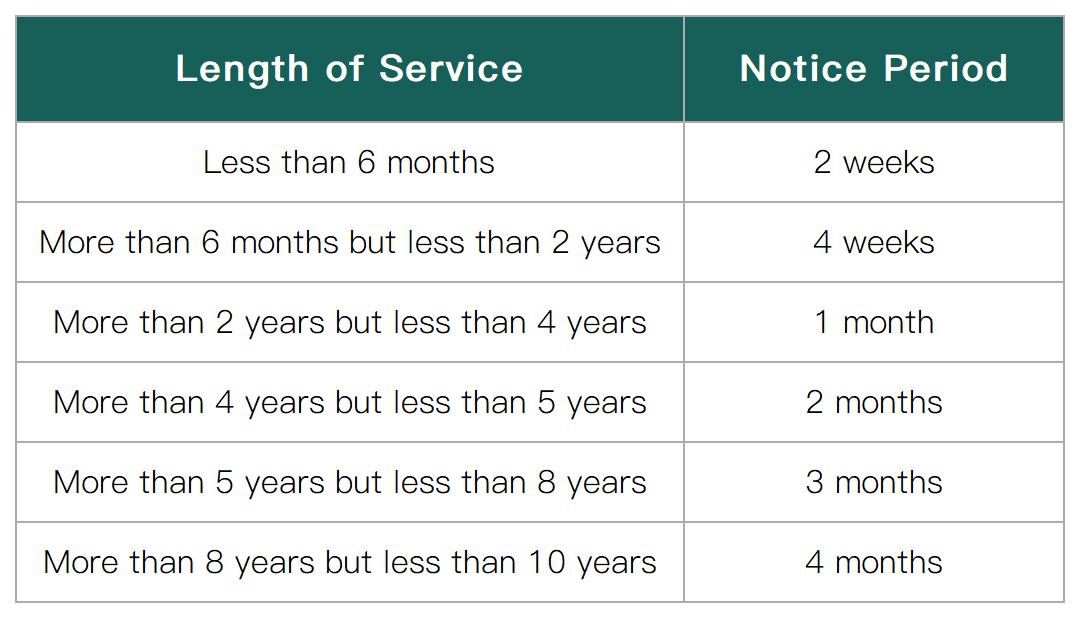
2. Notice period:
✦ According to the German Civil Code (BGB), the notice period for resignation depends on the employee's length of service in the company.
✦ The usual notice period is (calculated from the beginning of the month or the end of the month):
3. Compensation payment:
✦ There is no legal severance pay in Germany. Employees can only receive severance pay based on the social plan with the works council (usually agreed upon in the case of large-scale layoffs) or collective bargaining agreements.
✦ In practice, many employers and employees will agree on severance pay clauses to avoid lengthy court proceedings regarding the validity of the dismissal.
✦ The severance pay usually varies depending on factors such as the employee's length of service, salary level, and the reason for the termination of the contract.
 EOR
EOR GREC
GREC VISA
VISA PAYROLL
PAYROLL



 Home
Home
 Solutions
Solutions
 Resources
Resources
 Contact
Contact