The Republic of Singapore, commonly known as Singapore, is an island nation and city-state located in Southeast Asia. Singapore is composed of 63 islands, including Singapore Island, and has an area of 728 square kilometers. It is known as the "Garden City" due to its high level of greenery.
Singapore is known as one of the "Four Asian Tigers" and has a high per capita GDP and human development index. Currently, Singapore is an important global refining, trading, and logistics center, and also the largest international financial center in Asia. At the same time, it is also one of the countries with the highest population density in the world. Singapore is a multi-ethnic, multi-cultural, and multilingual country, and its national construction is based on civic nationalism.
Main Religions: Buddhism, Christianity, Islam, Taoism, Hinduism

The employment contract defines the relationship between the employer and the employee, including the terms and conditions of employment. The contract must include the Key Employment Terms (KETS) and basic terms such as working hours and job scope.
An employment contract is an agreement in which:
✦ One party agrees to employ the other party as an employee;
✦ The other party agrees to provide services to the employer as an employee.
Employers must provide KETS in writing to all employees who meet all the following requirements:
✦ The service contract is signed on or after 1 April 2016;
✦ Protected by the Employment Act;
✦ Employed for 14 days or more. This refers to the contract period, not the number of working days.
The main terms included in the employment contract are as follows:
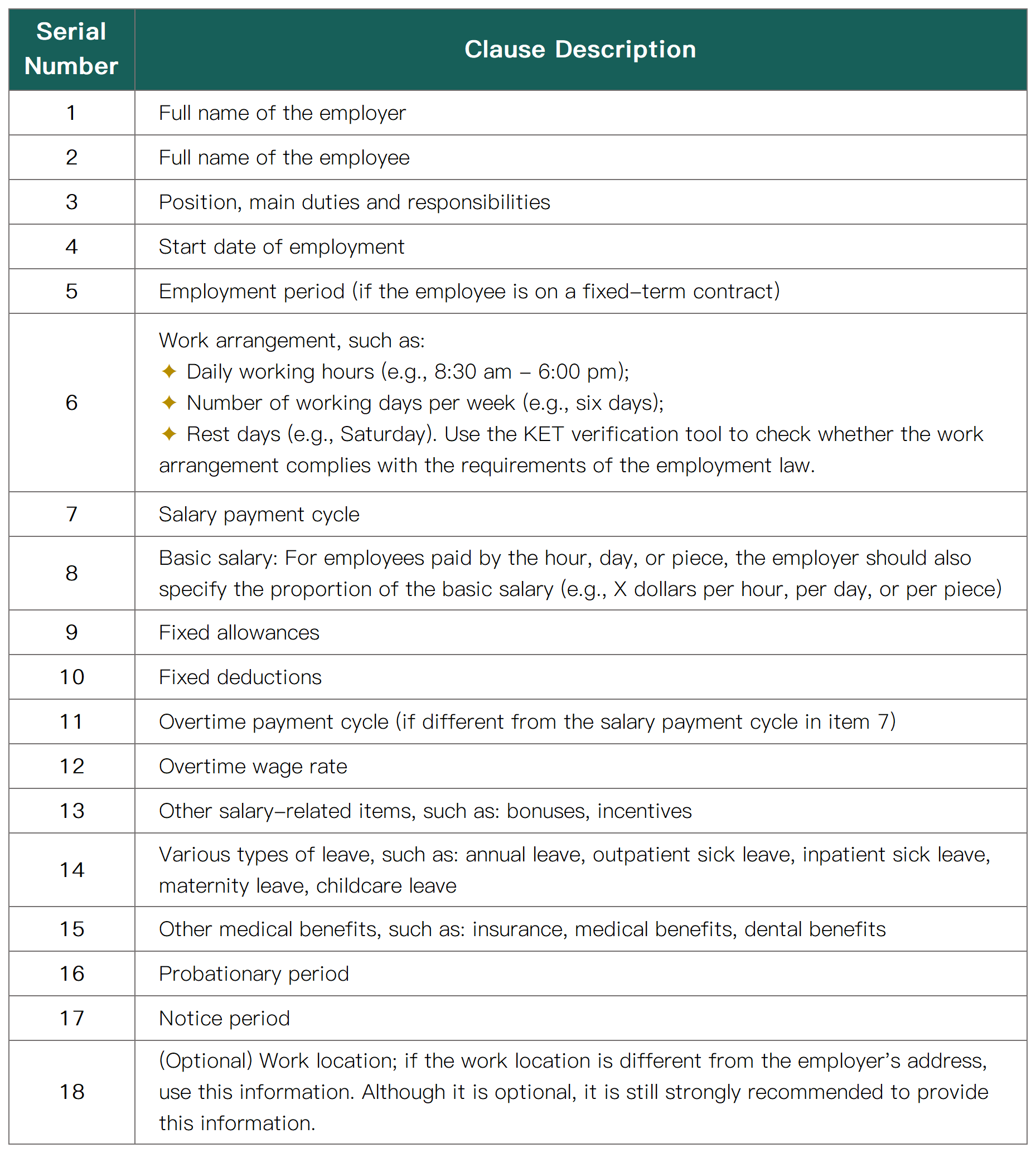
The employment contract can be oral or written. If the contract is in written form, all employers must provide a copy of the written employment contract to the employee. In addition, the employer must obtain the consent of the employee before making any subsequent changes to the terms of the employment contract. Signing a written contract is not mandatory. An oral contract still refers to the act. Therefore, workers are protected.
There is no explicitly stipulated probationary period in Singapore, and in practice, it is usually 3-6 months.
After working for 3 months, regardless of whether the employee is still in the probationary period, they can start enjoying paid annual leave.
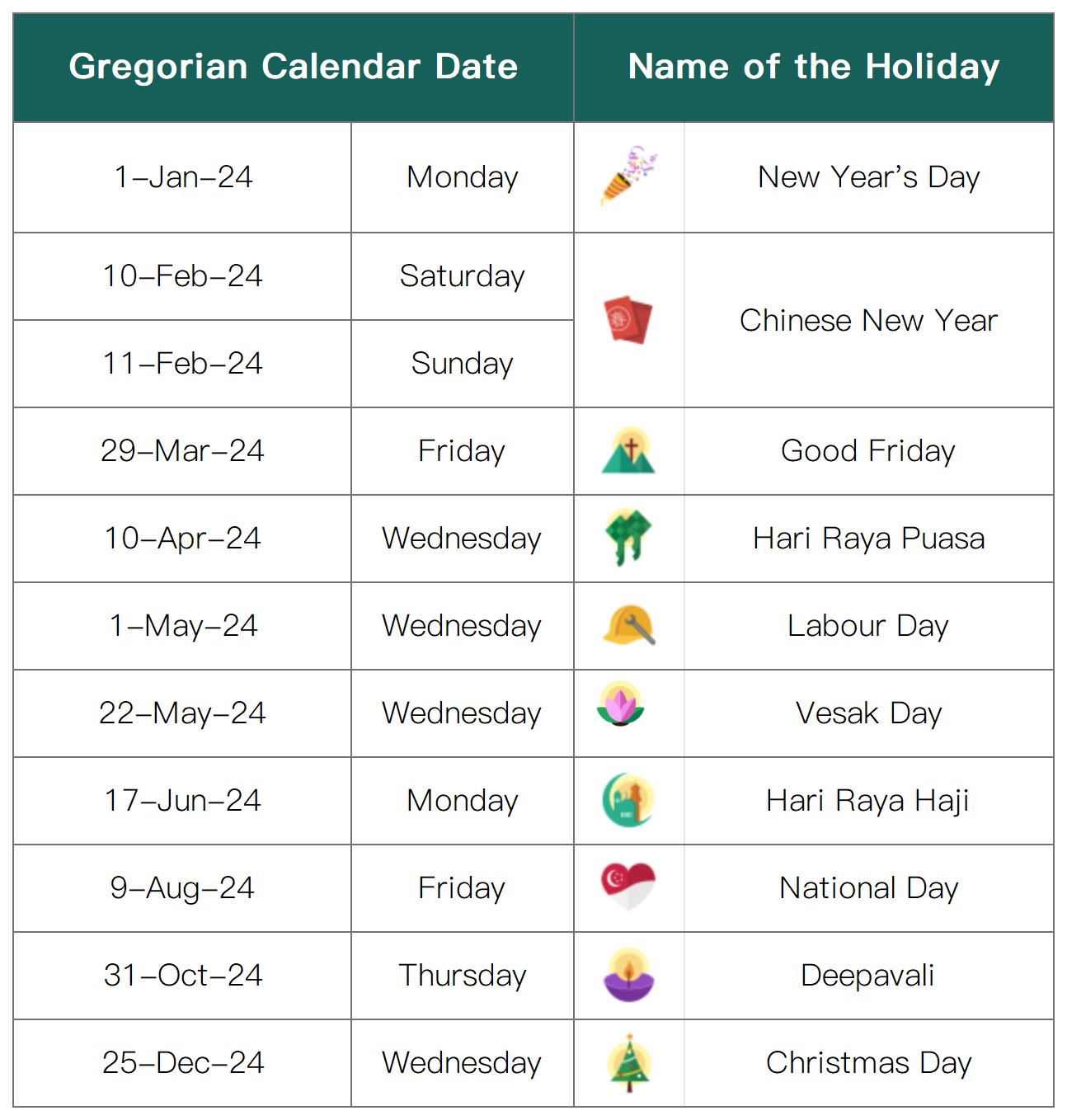
There are a total of 11 public holidays in Singapore in 2024, as follows:
1、Standard Working Hours:
✦ The daily working hours shall not exceed 8 hours, and the weekly working hours shall not exceed 44 hours. The working hours do not include breaks, tea breaks, or meal times.
2、Rest Time:
✦ Rest time: In general, the company cannot require employees to work continuously for more than 6 hours without providing a break; if the nature of the work requires it, and the employee works continuously for up to 8 hours, a meal time must be provided, and the rest time shall be at least 45 minutes.
✦ Employees can enjoy one day of rest per week. The company can choose Sunday or another day as the employee's rest day, and the rest day is not paid. If the company arranges the employee's rest day to be other than Sunday, it must arrange a work schedule and inform the employee at the beginning of the month. The interval between two rest days shall not exceed 12 days.
3、Overtime Hours:
✦ The total monthly overtime hours for employees shall be capped at 72 hours. Work on rest days or public holidays is not counted within the 72-hour overtime limit, except for work that exceeds the normal daily working hours on rest days or public holidays, and these additional hours are included within the 72-hour limit.
A、Overtime on Working Days:
Assuming that employees are entitled to overtime pay, including non-manual workers with a monthly salary of SGD 2,600 or less and manual workers with a monthly salary of SGD 4,500 or less.
The calculation of overtime pay is as follows:
Overtime Pay = Basic Salary per Hour × 1.5 × Total Overtime
HoursBasic Salary per Hour = (12 × Monthly Basic Salary) / (52 × 44)
B、Overtime on Rest Days:
Calculated as half a day or a whole day:
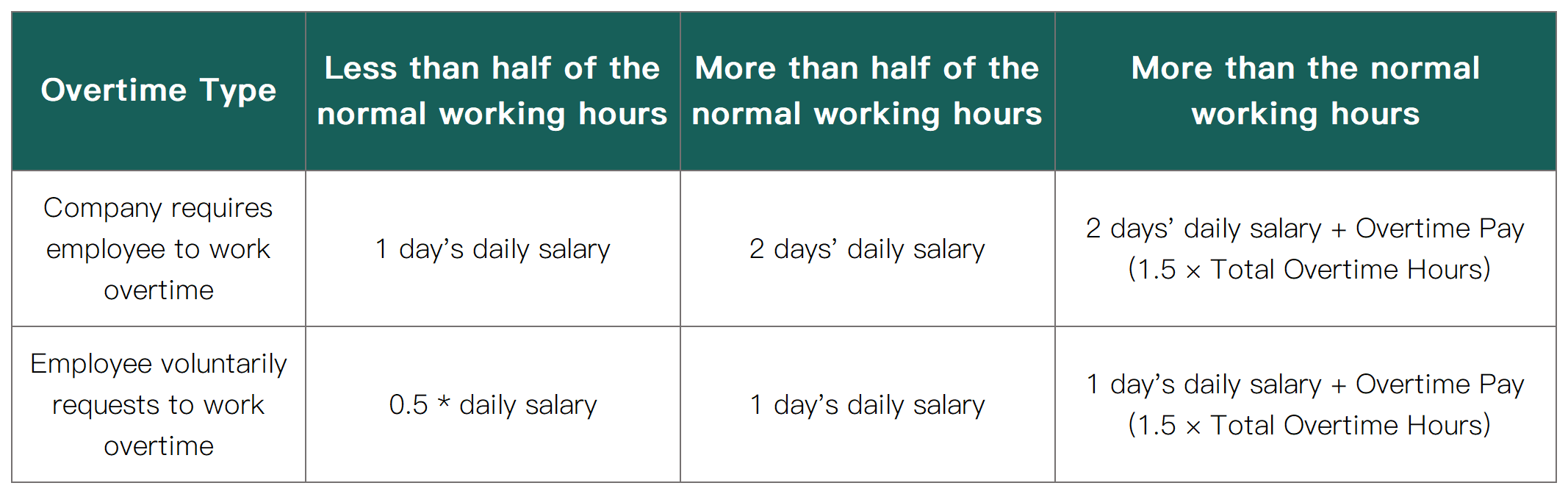
C、Overtime on Public Holidays:
If an employee is required to work overtime on a public holiday, the company will pay an additional day's daily salary, or the company and the employee may agree that the public holiday can be taken as compensatory leave on any working day after the overtime day.
1、Paid Annual Leave:
✦ The right to annual leave depends on the number of years the employee has worked for the employer. Employees can apply for annual leave after working for 3 months. The specific situation is detailed in the table below:
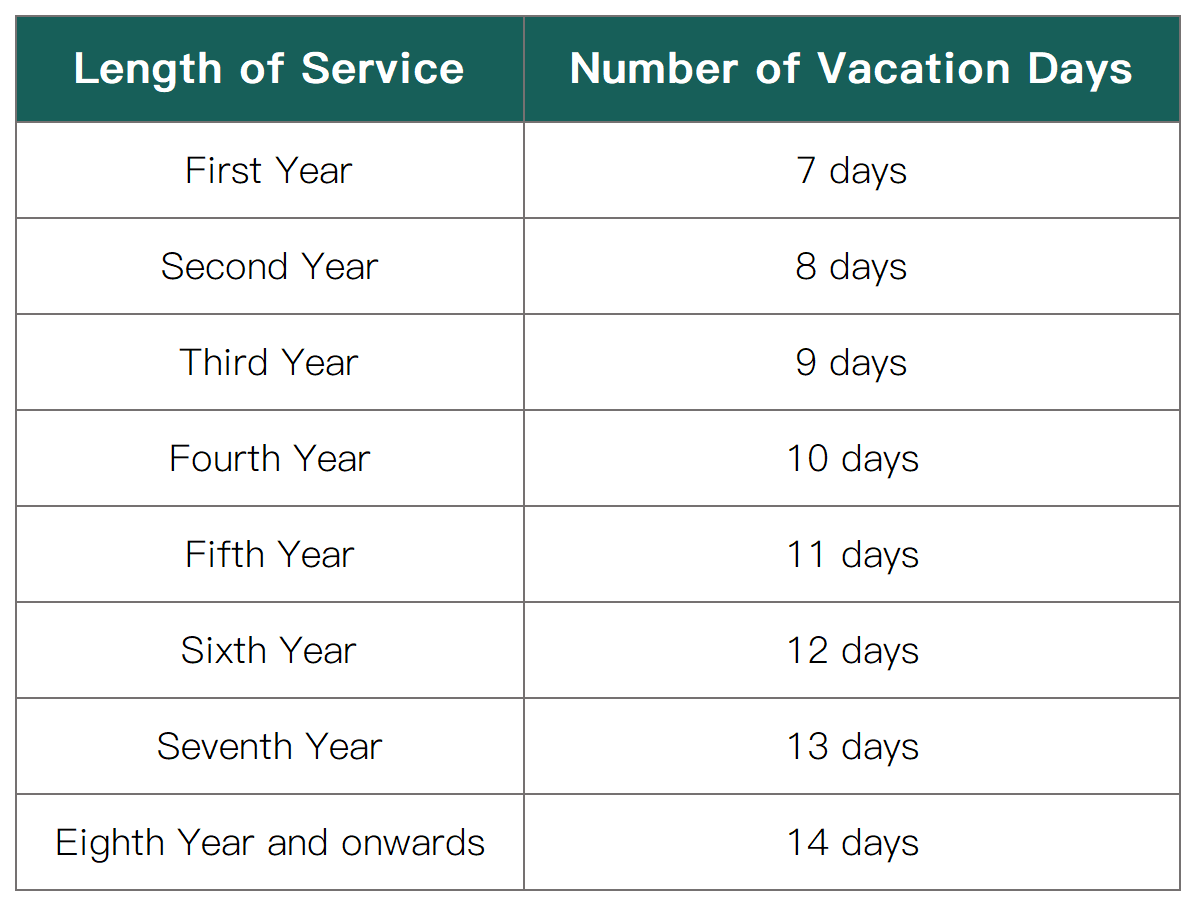
✦ If the employee has been employed for less than 1 year, it will be prorated:
Formula: (Number of completed service months ÷ 12 months) × Number of annual leave days
Note: If the number of days is less than half, it will be rounded down; if it is half or more, it will be rounded up to one day.
2、Sick Leave:
The number of paid sick leave days you are entitled to depends on your length of service. The maximum number of paid outpatient sick leave is 14 days, and the maximum number of paid inpatient sick leave is 60 days. The 60-day paid inpatient sick leave includes 14 days of paid outpatient sick leave.
✦ If the employee's length of service is within 3-6 months (less than 6 months), the entitlements will be calculated proportionally, as follows:
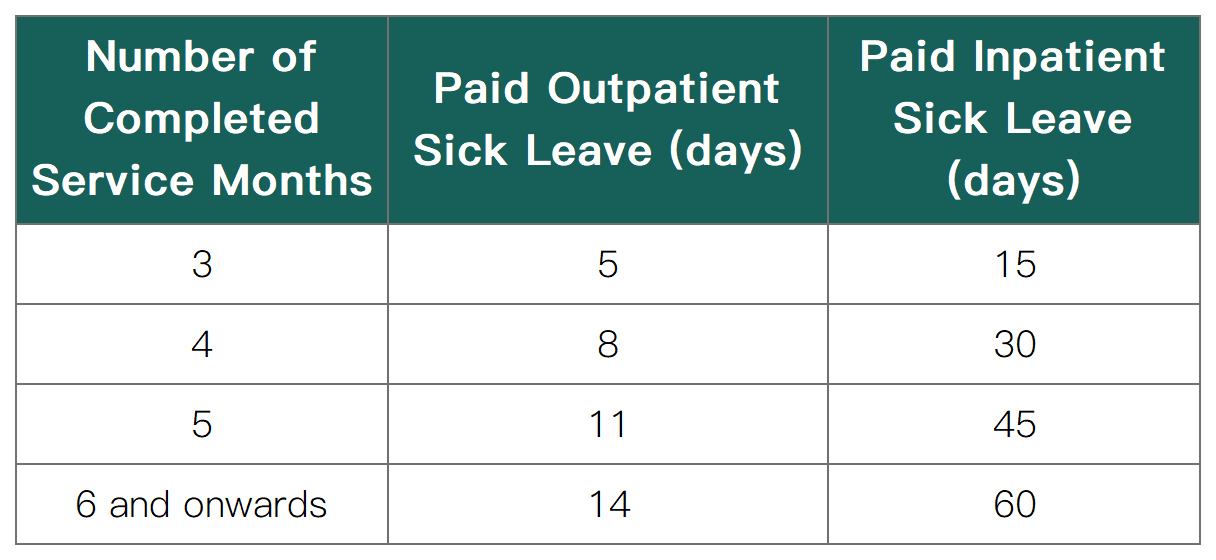
✦ If the employee has served for 6 months or more, they will enjoy the full sick leave rights.
The income tax rate in Singapore depends on an individual's tax resident status. An employee will be considered a tax resident if they are one of the following:
1、A Singapore citizen or Singapore permanent resident who resides in Singapore (except for temporary absences);
2、A foreigner who stays/works in Singapore:
✦ Stays in the previous calendar year for at least 183 days;
✦ For three consecutive years, even if the stay in Singapore in the first and/or third year may be less than 183 days;
3、A foreigner who has worked continuously in Singapore across two calendar years and has a total stay of at least 183 days*. This applies to employees entering Singapore, but excludes company directors, public entertainers, or professionals.
If the employee does not meet the above conditions, for tax purposes, the employee will be considered a non-resident in Singapore.
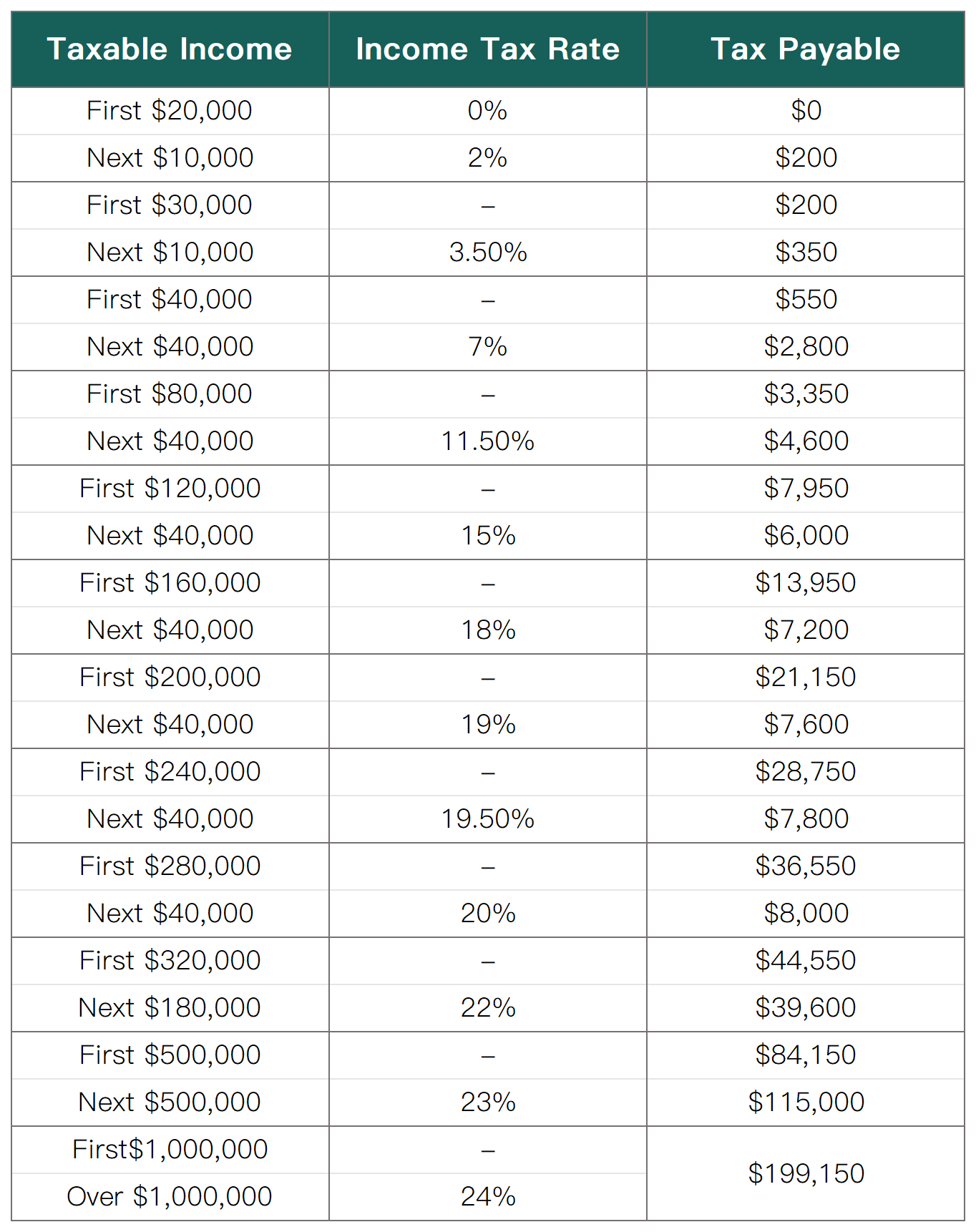
Note: The personal income tax rate for Singapore resident taxpayers is progressive. This means that high-income earners pay a higher proportion of taxes, and the current maximum personal income tax rate is 24%.
To achieve greater progressivity, the top marginal personal income tax rate in Singapore will be increased from the 2024 tax year. The portion of taxable income exceeding SGD 500,000 to SGD 1 million will be taxed at 23%, and the portion exceeding SGD 1 million will be taxed at 24%; both are higher than the current rate of 22%.
The resident tax rate table for Singapore in the 2024 assessment year is as follows:
The only government-mandated pension system in Singapore is the Central Provident Fund (CPF) system. It is a defined contribution system composed of funds contributed by employees and employers, as well as the interest accrued on the contributions.
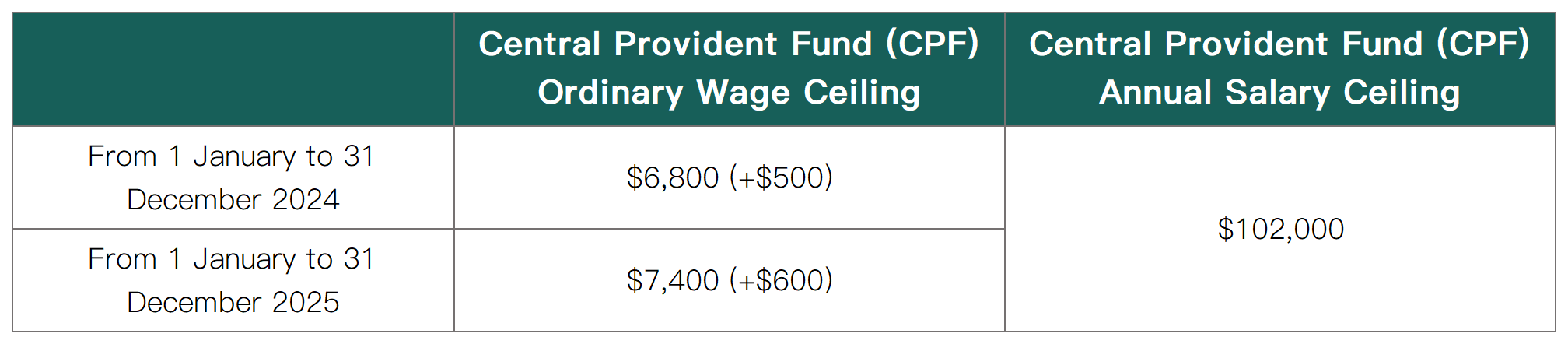
✦ By 2026, the ordinary wage ceiling for the Central Provident Fund (CPF) will be increased from S$6,000 to S$8,000. The first increase will be implemented on 1 September 2023. The increase will be carried out in four stages to allow employers and employees to adapt to these changes;
✦ The annual salary ceiling for the Central Provident Fund (CPF) will remain unchanged at S$102,000, which includes the maximum amount of CPF contributions for all wages (including ordinary wages and additional wages) within a year;
✦ The additional wage ceiling and the CPF annual ceiling will remain unchanged at [S$102,000 - the total ordinary wages subject to CPF contributions for the year] and S$37,740, respectively.
The CPF ordinary wage and annual salary ceilings from 2024 to 2026 are shown in the table below:
1、Contract Termination Notice:
✦ Any termination notice given by the employee or the employer must be in writing, otherwise it will be considered invalid.
2、Notice Period:
✦ If the employment contract specifies the employment period, when the employee resigns, they must:
a.Give advance notice in accordance with the corresponding notice period requirements, or
b.Compensate the employer by paying in lieu of notice.
✦ With the mutual consent of the employer and the employee, the notice period can also be waived and stated in writing.
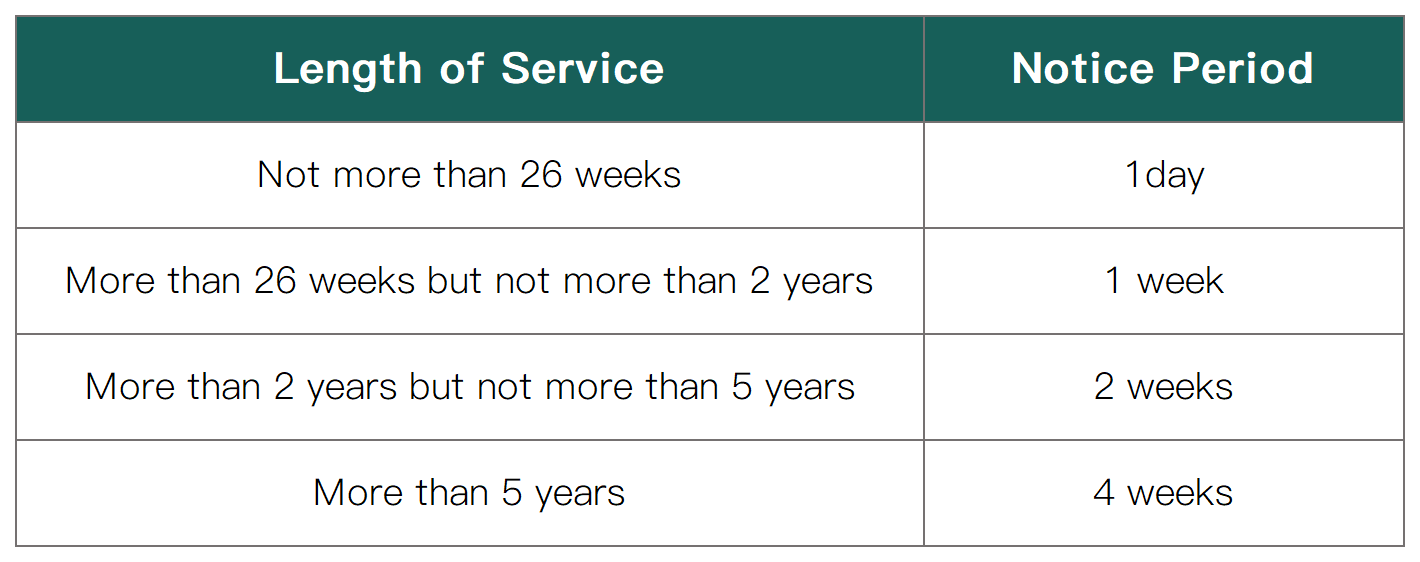
✦ If the notice period is not specified in the employment contract, the required notice period will depend on the length of service:
3、Compensation:
✦ Employees who have served the company for at least 2 years are eligible for severance pay; employees who have served the company for less than 2 years may receive an ex gratia allowance from the employer out of goodwill.
✦ The specific amount of severance pay depends on the provisions of the employment contract or collective agreement (for unionized companies). If there are no provisions, it must be negotiated between the employee (or the union) and the employer.
✦ Usually, the standard for severance pay is that the employee receives two to one month's salary for each year of service as compensation; companies with unions usually pay one month's salary for each year of service according to the corresponding provisions in the collective agreement as compensation.
 EOR
EOR GREC
GREC VISA
VISA PAYROLL
PAYROLL



 Home
Home
 Solutions
Solutions
 Resources
Resources
 Contact
Contact